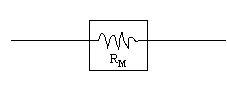
In this lab, first we will measure the internal resistance (RM) and the full scale current (IM) of a galvano meter. Then we will construct and check a voltmeter and ammeter.
Procedure:
Name: Date: Time:
Course:
METERS
Purpose: a. To measure the internal resistance (RM) and the full scale current (IM) of a galvanometer.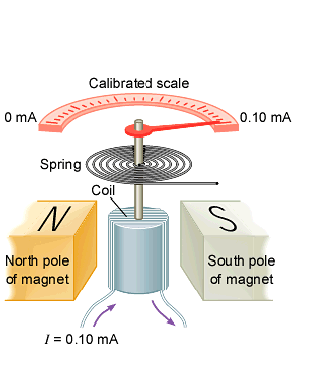
A galvanometer has two important characteristics that must be considered when
it is used as part of a measurement device. First, is the sensitivity of the
galvanometer. It is the amount of dc current that causes a full-scale deflection
(IM) of the pointer. The second important characteristic is
the resistance

In this
lab, first we will measure the internal resistance (RM)
and the full scale current (IM) of a galvano meter. Then we
will construct and check a voltmeter and ammeter.
Procedure:
A) To measure the internal resistance (RM) and
the full scale current (IM) of a galvanometer:
1.
Set up the following circuit and get the construction checked by the
constructor.
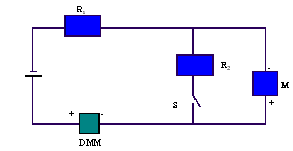
2. Set
R1 to 2999-ohm. With S open, adjust R1 by changing 100,
10, and 1 dials, to get a full scale deflection in the galvanometer. Record the
reading of the DMM, which is IM.
3. Close S and adjust R2 until the galvanometer deflects half
scale reading. Record the value of R2, which is equal to
RM.
Full scale current of the galvanometer, IM =
Internal resistance of the galvanometer, RM =
4. Explain why R2 = RM in procedure 3. __________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
B) Construction of a voltmeter: A resistance is placed in series with a galvanometer to convert it to a voltmeter as shown below.
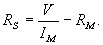
The
potential difference or voltage (V) across the meter and series resistance is
given by,
V = IM (RM + RS).
![]()
1. Calculate the series resistance
Rs for a 10-volt voltmeter. Rs =
_______________.
2. To construct the voltmeter; connect the resistance,
Rs in series with the galvanometer. Use a decade box for
Rs.
3. Set up the following circuit to measure voltages. Get the circuit checked
by the instructor.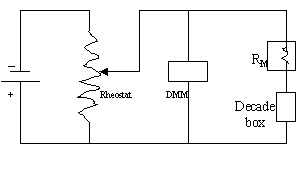
4. The constructed voltmeter should read full scale for
10 volt.
5. Change the voltage and complete the following table.
| Voltmeter reading ( V ) | Constructed voltmeter reading |
| 0 | |
| 2 | |
| 4 | |
| 6 | |
| 8 | |
| 10 |
C) Construction of an ammeter: A resistance (Rp) is placed in
parallel with the galvanometer to convert it to an ammeter as shown below.
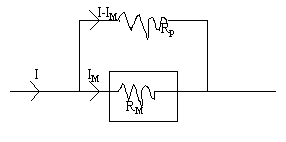
(I - IM) Rp = IM RM
![]()
1. Calculate the parallel resistance, Rp for a 500-mA ammeter. Rp = _____________
2. Calculate the length (L) in cm of #30-Cu wire required to obtain Rp. L = _____________
![]() Diameter (#30) = 0.02548 cm, Resistivity of Cu = 1.72 x 10-6ohm. cm.
Diameter (#30) = 0.02548 cm, Resistivity of Cu = 1.72 x 10-6ohm. cm.
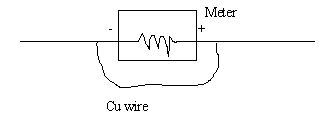
3. Cut a piece of #30-Cu wire of length (L+5) cm.
4. Construct the
ammeter by connecting the Cu wire in parallel with galvanometer, as shown
below.
.5. Set up the following circuit to measure currents.
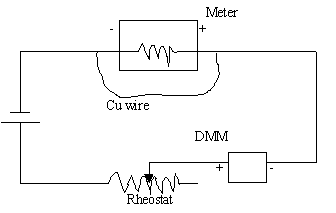
6. Get the circuit checked by the instructor.
7. The constructed ammeter should deflect full scale for 500 mA. If not adjust the length of Cu wire to get full scale deflection.
8. Change the current and complete the following table.
| amtmeter reading (mA) | Constructed amtmeter reading |
Problems:
1. A galvanometer has a full-scale current of 0.100 mA and a coil resistance of 50.0 ohm. This instrument is used with a shunt resistor to form an ammeter that will register full scale for a current of 60.0 mA. Determine the resistance of the shunt resistor.
2. A voltmeter utilizes a galvanometer that has a 180- ohm coil resistance and a full-scale current of 8.30 mA. The voltmeter measures voltages up to 30.0 V. Determine the resistance that is connected in series with the galvanometer.