Internal Resistance and Discharge Characteristics of a
Name:____________________________ Partners:_______________________
A. Internal Resistance
Purpose: Determine the internal resistance of a C-cell battery.
Apparatus: C-cell, C-cell holder, DMM, decade resistance box, and connecting wires.
Theory:
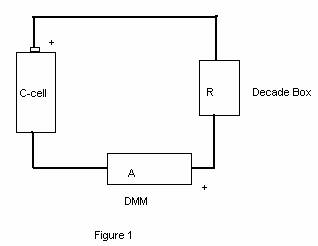
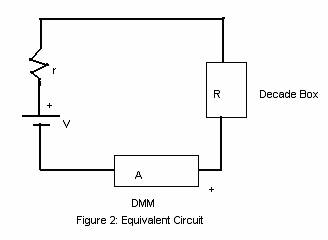
Procedure:
1. Apply Ohm's law to the above equivalent circuit. Use the symbol, I for current.
____________________________________________
2. The current, I in the circuit will be measured by changing the resistance R of the decade resistance box.
3. Change the variables (R and I) to obtain a linear plot. Identify how you will determine the cell voltage, V and the internal resistance, r from your plot.
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
_____________________________________________
4. Measure the cell voltage by connecting a DMM directly to the C-cell.
5. Set the resistance to 10 ohm in the decade box using the X1 dial. Set all
other dials to zero.
6. Set up the circuit shown in Fig. 1 and have your construction checked by the instructor.____________________
7. Collect the current and R data.
8. Enter your data in Excel, create a new column for the transformed variable, and plot a linear graph. Print a hard copy.
9. Obtain the cell voltage, V and the internal resistance, r from your plot.
DATA: Cell voltage (using a DMM) = V =
______________
|
R (ohm) |
I (A) |
|
10 |
|
|
9 |
|
|
8 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
5 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
3 |
|
The cell voltage, V and the internal resistance, r from your plot:
V = ______________ r = ___________________
B. Discharge Characteristics
Purpose: Investigate the discharge characteristics of a C-cell battery.
Apparatus: PC with
Theory: The discharge characteristics will be investigated by observing the current through and the voltage across the battery as it is used to light a light bulb.
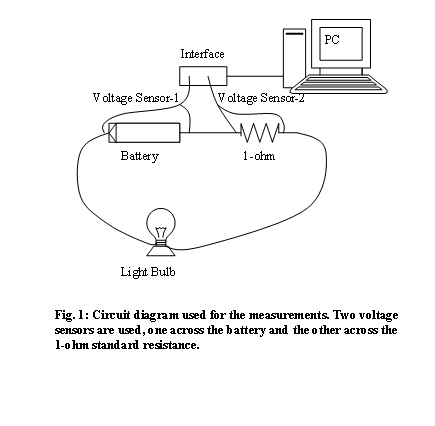
As can be seen in the above diagram, the battery, light bulb, and 1-ohm resistance are connected in series. The voltage across the battery will be monitored by voltage sensor-1 and the voltage across the 1-ohm resistance will be monitored by voltage sensor-2. The magnitude of the current is equal to the magnitude of the voltage across the 1-ohm resistance, since R = 1 in the equation V = I x R.
The amount of charge discharged by the battery is equal to the product of current and time, which can be also be determined by finding the area under the Current VS. Time graph.
Procedure:
- Unscrew the light bulb and Set up the above circuit.
- Open DataStudio, click Create Experiment, and double-click Voltage Sensor under the Sensors. Double-click Voltage Sensor one more time to activate the second voltage sensor.
- Open the Sensor Properties window by double-clicking one of the voltage sensor icons displayed as connected to the 750-interface.
- Change the sample rate to slow and set 10 seconds between samples.
- Click the Graph display and choose ChA.
- Screw in the light bulb and click Start.
- Collect data for about 5 minutes and stop the data collection. Unscrew the bulb.
- Double click the Table display and choose ChA.
- High-light and copy Voltage VS. Time data and paste it in a blank Excel spread sheet.
- Double click the Table display and choose ChB.
- High-light and copy this data also in the 3rd and 4th column of the same excel spread sheet.
- In the Excel spread sheet, for the ChB data: delete the time column and re-name voltage as current.
- Calculate the charge, discharged by the battery in the last column.
- Plot Voltage VS. Time and Current VS. Time.
- Write a conclusion.