Speed of Sound in Air Name:_____________________________
Partner(s):___________________________ Course: ________________ Time:_______
A. Resonance Method
Purpose: To investigate air-column resonance and determine the speed of sound in air.
Apparatus: Resonance tube apparatus, audio signal generator, speaker, stand w/clamp, and water.
Theory: In wind instruments the wind (air) is made to resonate. Resonance makes the sound audible. In this investigation a small speaker, connected to an audio signal generator, will generate sound of required frequencies. The speaker is held above the open end of the resonance tube, which has water. The water level can be changed by lowering/raising the reservoir can.
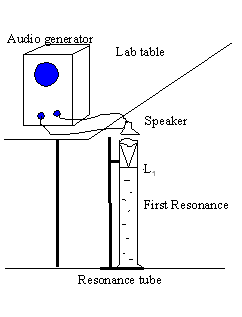
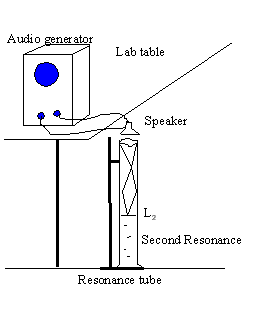
As you lower the water level, keep your ear next to the speaker and listen carefully. At the first resonance, L1 the sound will be louder. If you keep on lowering you will hear the loud sound again at the second resonance, L2. The wavelength, λ is given by: λ = 2 (L2 - L1). The speed of sound in air, V is given by: V = λ∙f, f = frequency.
Question: Approximately where will the second resonance point compared to
the first resonance point. Explain your answer.
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
DATA
|
Dial |
First |
Second Resonance Point, L2 |
Change in Resonance Points, L2-L1 |
Wavelength, λ |
Speed of sound, V |
|
400 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
500 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
|
600 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
B. Temperature Method
Purpose: Determine the speed of sound in air using temperature.
Apparatus: PC with interface and temperature sensor.
Theory: Speed of sound in air (in m/s) at temperature T (in Kelvin) is given by;
![]()
where γ = 1.40, m = 4.8 x 10-26 kg, and k = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K.
Procedure:
1) Measure the room temperature using a temperature sensor, interface, and PC and calculate the speed of sound.
a. Make sure that the power for the interface is turned
on.
b. Plug in the temperature sensor to analog channel A, white
arrow on top.
c. Double-click the DataStudio icon in the desktop.
d. Click Create Experiment.
e. Scroll down the sensors and click on Temperature Sensor.
f. Double-click the digit display and click start.
DATA:
Room temperature, t = ___________0C = _________K.
Speed of sound (using temperature) = V = ____________
C. Echo Method
Purpose: Determine the speed of sound in air using a sound sensor.
Apparatus: Sound sensor, interface, PC, long cardboard tube, lab stand, and meter stick.
Theory:
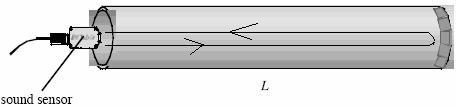
If the length of the tube is L, then the round trip distance of travel is 2L. If the travel time is t, then the speed of sound, v is given by;
![]()
Procedure:
1. Connect the sound sensor to the interface.
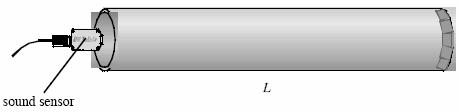
2. Place the cardboard tube on the laboratory table and set up the sound sensor using a lab stand close to the open end as shown below.
3. Double-Click (DC) the DataStudio icon.
4. DC Open Activity and DC P27, Speed of sound.
5. DC the Voltage Scope under Displays.
6. Move the mouse over the trigger symbol (![]() )
until a hand appears, click and drag it up by about 1 division (1 volt) as
shown below.
)
until a hand appears, click and drag it up by about 1 division (1 volt) as
shown below.
7. Click Start, and snap your fingers at the open end of the tube as shown below.
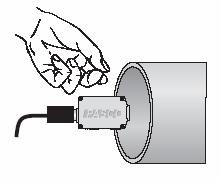
8. If the data is not captured as shown below, repeat
procedure 7. The pulse should be compact and the beginning crest/trough of the
initial pulse and the echo should be clearly visible.
Show the display to the instructor. _____________________
9. If the display is approved by the instructor, click the
Transfer Data button (![]() ).
).
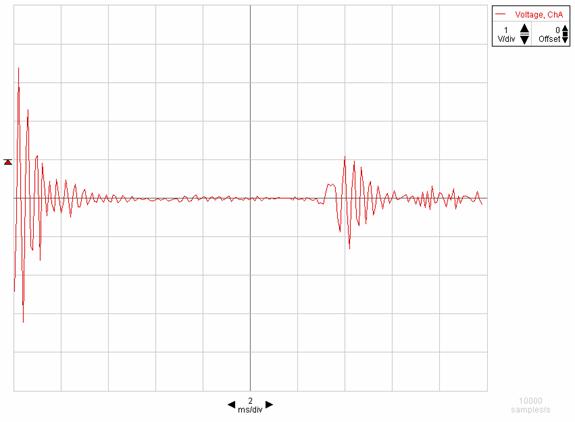
10. DC the Graph display, click/highlight Data, and Click OK. Your data should look something like as shown below.
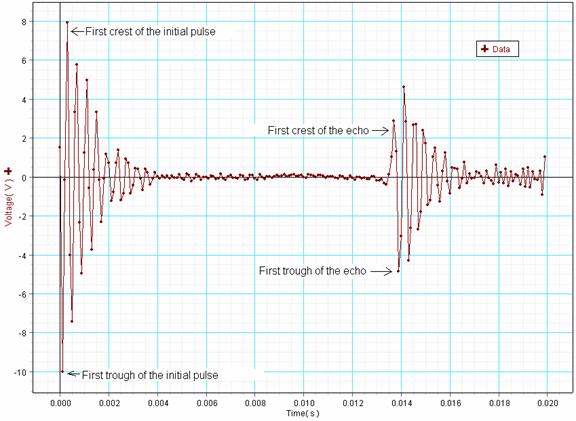
11. Observe the initial pulse and its echo and determine whether the echo is in phase or out of phase of the initial pulse.
__________________________
12. Which one(s) of the following is (are) the correct travel time (s)?
a. The time interval between the first crest of the initial pulse and the first trough of the echo.
b. The time interval between the first crest of the initial pulse and the first crest of the echo.
c. The time interval between the first trough of the initial pulse and the first trough of the echo.
d. The time interval between the first trough of the initial pulse and the first crest of the echo.
13. Use the smart tool to find the travel time and complete the data table below.
|
Length of tube (m) |
Round trip travel Distance (m) |
Travel Time (s) |
Speed of sound (m/s) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14. Compare and contrast the above methods (A, B, and C) of
measuring the speed of sound in air.