Interference and Diffraction Name:_______________________
Partner(s):_____________________________________________
A. Double-Slit Interference
Purpose: To observe double-slit interference pattern and measure the wavelength of light.
Apparatus: Light sensor with aperture bracket, diode laser w/power adapter, multiple-slit set, optics bench, rotary motion sensor, linear translator, 750-interface, and PC.
Theory:

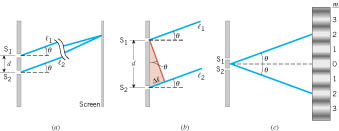
Bright fringes of a double-slit are given by (d is double-slit separation and λ is wavelength),
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Procedure:
1. Place the optics bench on the laboratory table.
2. Remove the rack from the linear translator by unscrewing the two rack thumbscrews.
3. Attach the base of the linear translator to the optics bench, close to the 0-cm end.
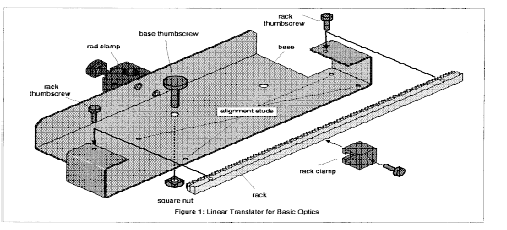
4. Insert the rack through the slot in the side of the rotary motion sensor. Put the rack back and tighten it with rack thumbscrews.
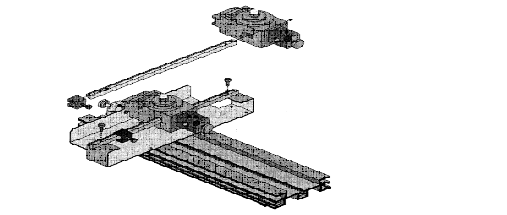
5. Attach the light sensor with aperture bracket to the rotary motion
sensor.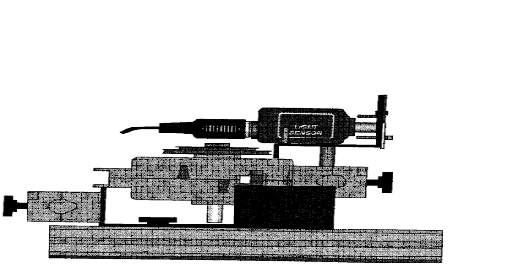
6. Mount the diode laser on the other end (close to 100-cm) of the optics
bench. 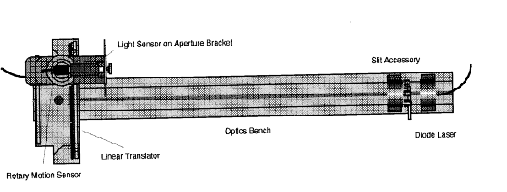
7. Set the multiple slit to a double slit separation, d of 0.25 mm and place the double-slit in front of the diode laser.
8. Plug in the power adapter for the laser.
9. Adjust the position of the light sensor so that the laser beam strikes in the middle of the aperture bracket-1.
10. Move the rotary motion sensor/light sensor so that the interference pattern is away from aperture bracket-1 and attach the rack clamp.
11. Connect the rotary motion sensor to digital channels 1 (black) and 2 (yellow).
12. Set the gain to 100 in the light sensor and connect it to analog channel A .
13. Open DataStudio, click Open Activity, click Library, click Physics Labs, and click P35 Diffraction.
14. Open the Light Intensity VS. Position graph display.
15. Click Start, and slowly and smoothly move the rotary/light sensor so that the whole interference pattern passes through the sensor.
16. Stop recording data and maximize the graph display.
17. Show the graph to the instructor.
18. Count the # of fringes and measure the whole width with smart tool.
19. Print a hardcopy of the interference pattern.
20. Close DataStudio, without saving.
Data: Double-Slit Interference
# of fringes = N = _________
Width for the above # of fringes = __________
Fringe-width = Y = __________
Double-Slit separation = d = _________
Double-Slit to Screen distance = L = __________
Wavelength (measured) = λ = dY/L = __________
Wavelength (accepted) = λ = ___________
% Error = ____________
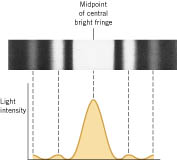
B. Single-Slit Diffraction
Purpose: To observe single-slit diffraction pattern and measure the wavelength of light.
Apparatus: Light sensor with aperture bracket, diode laser, single-slit set, optics bench, rotary motion sensor, linear translator, 750-interface, and PC.
Theory:
 |
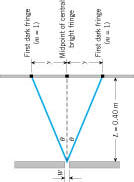 |
Dark fringes for the single-slit diffraction are given by (w is the single-slit width and λ is wavelength),
![]()
![]()
![]()
Procedure:
1. Remove the double-slit and replace it with a single-slit set to slit-width, a = 0.16 mm.
2. Open DataStudio, click Open Activity, click Library, click Physics Labs, and click P35 Diffraction.
3. Open the Light Intensity VS. Position graph display.
4. Click Start, and slowly and smoothly move the rotary/light sensor so that the whole interference pattern passes through the sensor.
5. Stop recording data and maximize the graph display.
6. Show the graph to the instructor.
7. Measure the width of the central bright fringe.
8. Print a hardcopy of the diffraction pattern.
9. Close DataStudio, without saving.
Data: Single-Slit Diffraction
Width for the central dark fringe = 2Y = __________
Half-width for the central dark fringe = Y = ________
Single-Slit width = w = _________
Single-Slit to Screen distance = L = __________
Wavelength (measured) = λ = wY/L = __________
Wavelength (accepted) = λ = ___________
% Error = ____________